Introduction
What is WoolyAI?
WoolyAI is a GPU hypervisor for ML giving portability, high utilization, and concurrency without changing your existing CUDA code. It lets you develop and run CUDA/PyTorch apps anywhere (even CPU-only machines) while the actual kernels run remotely on AMD or NVIDIA GPUs. It compiles your kernels into a Wooly Instruction Set ("WIS") on the client, then JIT compiles to native CUDA or ROCm on the GPU server.
- Vendor-agnostic execution: Same Unified ML container to run on NVIDIA or AMD backends.
- CPU (Client) / GPU (Server) split:
- Wooly Client (on your CPU-only machine) captures CUDA kernels → emits WIS → sends WIS to the WoolyAI Server (on GPU nodes) for execution.
- Wooly Server (hypervisor) (on GPU nodes) converts WIS → native GPU ISA and executes.
- Dynamic scheduling: Measures and allocates at runtime GPU cores/VRAM across concurrent process (jobs) with deterministic scheduling options.
- Memory efficiency: VRAM dedup (e.g., shared base model weights across many LoRA adapters) to pack more models per GPU.
- Ecosystem-friendly: Works with your existing PyTorch scripts — no model/code rewrites.
Advantages
- Disaggregate CPU execution from GPU in ML Containers: Access high-end heavy-weight GPUs from lightweight (non-GPU) local machines. Researchers can run PyTorch or CUDA code on their CPU-only machines with no local GPU.
- Eliminate driver/toolkit mismatch headaches: Single Unified Client Container which runs ML workloads and sends kernel requests to GPUs separately. You'll no longer need to install and constantly manage NVIDIA drivers, CUDA versions on your dev environment to match with the GPU server runtime stack.
- Tight control over security and governance: Developer machines don't need GPU drivers or device files since execution happens on the WoolyAI Server, remotely. Think of a "thin client" model.
- Lower Infrastructure Costs: Single Unified container that can run ML workloads on both Nvidia and AMD without any changes, providing flexibility to choose the cheapest (or whatever is even available) hardware.
- Maximizing GPU Utilization
- True GPU Concurrency: Runs multiple kernel executions in a single GPU context without time-slicing overhead, unlike traditional static partitioning (MIG/MPS) that create rigid, underutilized segments.
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: Real-time redistribution of GPU cores and VRAM based on active kernel processes, priority levels, and actual usage patterns -- not fixed quotas.
- 100% GPU Utilization: Eliminates idle cycles by continuously analyzing and optimizing resource distribution, ensuring no GPU compute sits unused.
- Memory Sharing: Share identical model in VRAM across multiple workloads to optimize VRAM usage.
Architecture
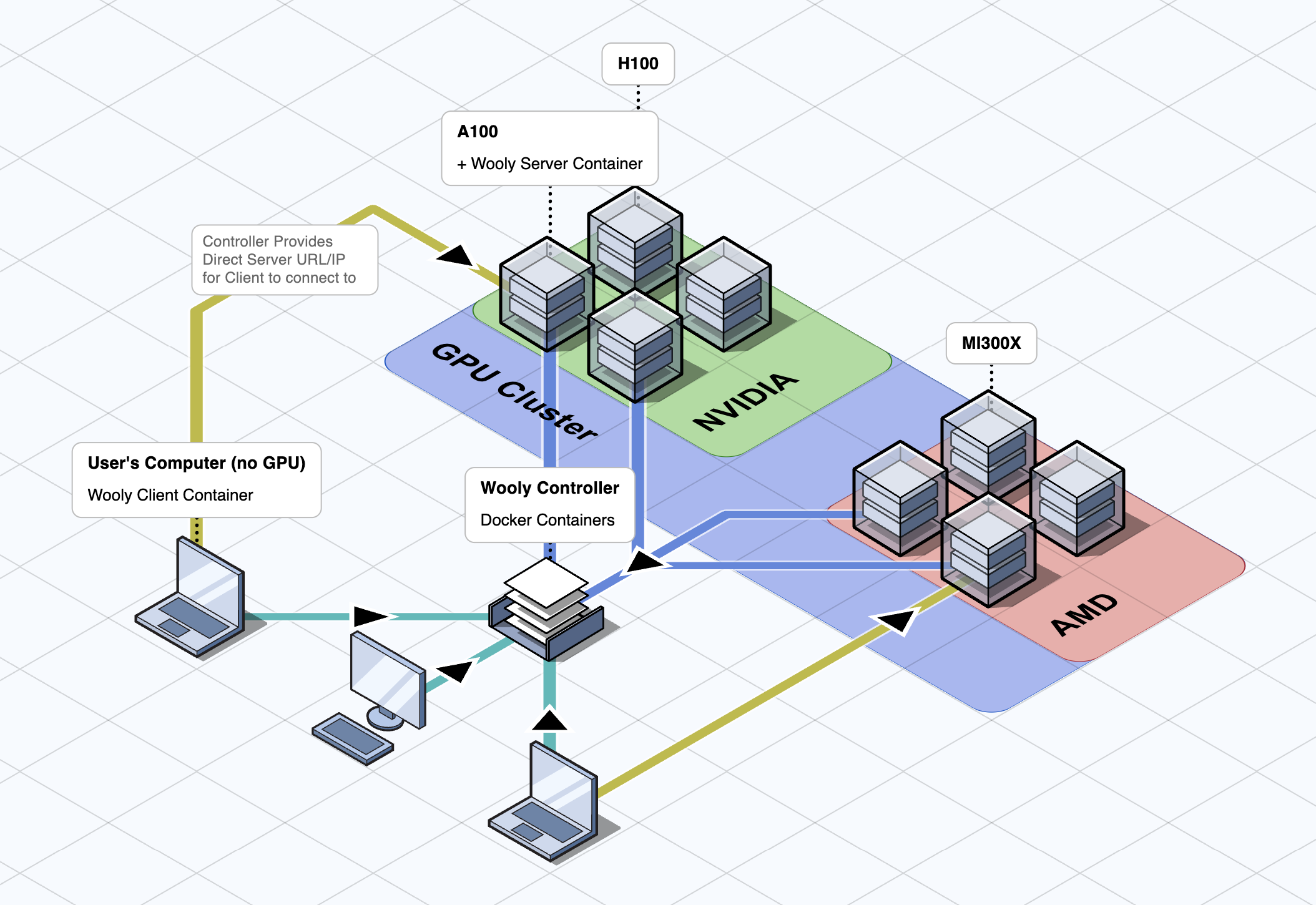 High Level WoolyAI Architecture diagram showing the three main components: The WoolyAI Client, The WoolyAI Server, and The WoolyAI Controller.
High Level WoolyAI Architecture diagram showing the three main components: The WoolyAI Client, The WoolyAI Server, and The WoolyAI Controller.
It has three main components:
- The WoolyAI Client is a docker container inside which you run your Pytorch scripts and other ML workloads. It can run anywhere, even machines without a GPU, supporting remote GPU execution to the WoolyAI Server. It sends execution request to the Wooly Controller which then identifies the most efficient GPU from your cluster for execution.
- The WoolyAI Server is a docker container that runs on each (single/multi) GPU servers and performs execution request from Wooly Clients to ensure maximum GPU utilization at all times. Wooly Server are connected to Wooly Controller and regularly reports back GPU usage metrics.
- The WoolyAI Controller is a web interface and router for routing execution requests from multiple Wooly Clients (ML jobs) across a multi node (GPU hosts) cluster. If your setup only has a single GPU, you can skip controller configuration. WoolyAI Controller identifies which GPU node(host) and which GPU on that node, the Wooly Client request should go based on the following GPU utilization metrics - Utilization and Starvation percentage. A GPU with high Starvation percentage means GPU idle time is very low and it's processing multiple jobs efficiently.
What is the WoolyAI Client?
The WoolyAI Client is a docker ML container you can run on GPU-less/CPU-only machines. It can be connected to the WoolyAI Controller (through config file), and when a GPU (CUDA) kernel is started, the WoolyAI Controller will return the URL/IP of a WoolyAI Server that the Client will actually connect to execute the kernels on.
What is the WoolyAI Server?
The WoolyAI Server is a container you'll run on all of your GPU hosts. It receives the GPU kernels from the WoolyAI Client and executes them on the GPU(s) for cross-vendor (Nvidia or AMD) CUDA execution and maximizing per-GPU usage at all times.
Just like the Client, you'll connect your WoolyAI Server to the WoolyAI Controller. At that point, the Controller will be able to route execution requests to the WoolyAI Server based on real-time GPU utilization metrics.
GPU Utilization benefits are therefore twofold:
- The best GPU in your cluster is selected for the incoming execution request by the WoolyAI Controller based on real-time GPU utilization.
- The kernel executions are dynamically allocated GPU resources once running on a WoolyAI Server.
What is the WoolyAI Controller?
The WoolyAI Controller is optional if you only have a single GPU setup. In this scenario you will configure Wooly Client to talk directly to the Wooly Server running on your single GPU host. WoolyAI Controller is required if you have more than one GPUs in your cluster.
The WoolyAI Controller is a web interface and router. Multiple GPU nodes running the WoolyAI Servers are joined to the Controller and constantly send telemetry about available GPU usage. The WoolyAI Client and Server are both connected to it, so the Controller can dynamically route execution requests to the best GPU node running the WoolyAI Server based on real-time GPU utilization.